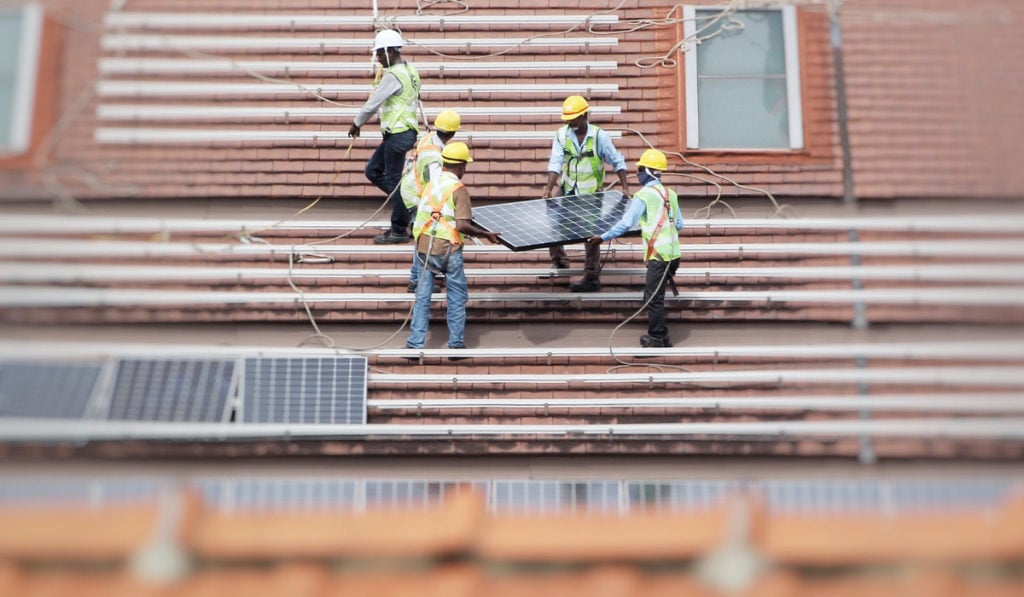
Grounding issues and damaged modules are the most common safety problems among rooftop solar projects, according to Clean Energy Associates (CEA).
In a recent report, CEA stated that it had performed over 600 rooftop PV safety audits in 14 countries, with 97% of them boasting major safety concerns. Almost half (49%) of the projects had grounding issues which usually took place at the inverter or equipment pad, between PV array blocks and module rows where short conduit runs were needed, and on extended conduits runs, which require additional grounding straps.
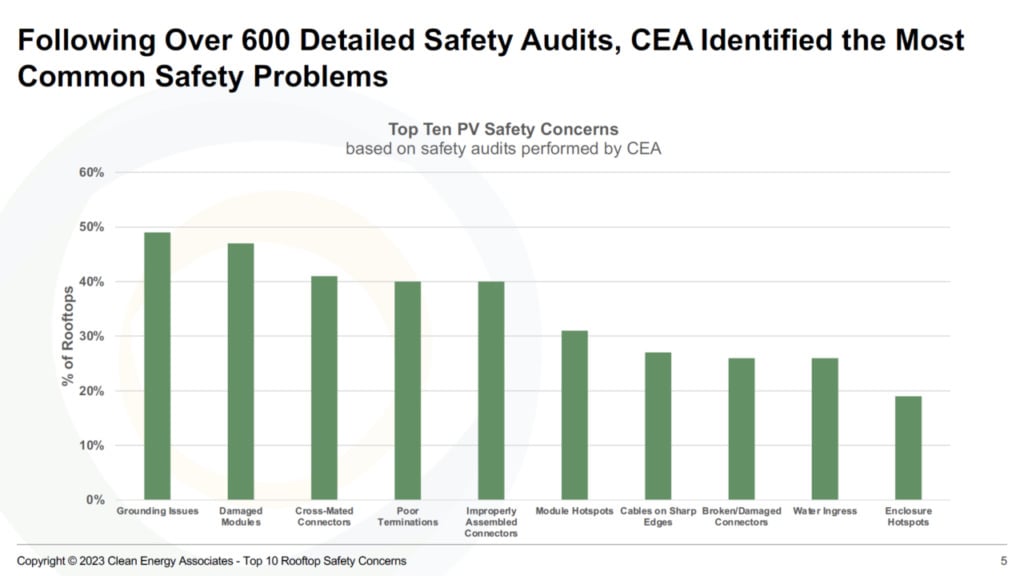
Grounding issues were caused by incorrect designs, moisture or water intrusion, installation plans not followed by the crew, and problems overlooked by installation quality control personnel.
These factors could lead to several consequences, such as hazardous equipment current leakage and increased maintenance and system down time from inverter faults. But more importantly, it could endanger onsite personnel.
After grounding issues, 47% of rooftop PV projects had damaged modules. Incorrect installation or cleaning methods, including walking on modules, were one of the major reasons why. Extreme weather like hail or wind, electrical short circuits in the module leading to thermal events, and heavy soiling or grease on the modules affecting performance were amongst the factors that could damage the modules.
Damaged modules could lead to microcracking and soiling that lower the performance of modules, electrical fault and shock, and fire safety risks.
Cross-mated connectors were the third most common safety problem, which had been caused by incorrect understanding of Underwriters Laboratories-listed connector pairings, incorrect installation techniques, undertrained installation technicians, and improper field made connectors which don’t match the module connector.
Having cross-mated connectors could lead to water intrusion and corrosion, along with arcing in connector housing, potentially leading to a fire.
Other safety concerns included poor terminations (40%), improperly assembled connectors (40%), and module hotspots (31%).





